Abstract
Background
Primary bone diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a variant of extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) that is relatively rare, accounting for 3-15% of extranodal NHL and less than 1% of all NHL. Patients often present with pain and swelling or pathologic fracture of the affected area of the skeleton, and B symptoms are often less prevalent. Many cases are limited stage at presentation. Patients are usually treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or similar induction therapy. Based on older studies showing improved outcomes associated with the addition of radiation (many completed prior to the rituximab era), patients often still receive combined-modality therapy today. However, it remains unknown whether consolidative radiation therapy (RT) confers additional benefit following rituximab-based chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) induction. We sought to address this question in a multicenter retrospective study.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis of outcomes in a modern cohort of patients who underwent treatment for primary bone DLBCL using chemotherapy regimens in the rituximab era either with or without consolidative RT. Data was collected from 13 academic medical centers in the U.S., with patients treated between 2005 and 2019. Patients were identified using each institution's hematologic malignancy registries. Analysis was limited to patients with primary bone DLBCL, with stage I-II disease (primary site +/- locoregional lymph nodes) that could be encompassed in a radiation field. Patients who received CIT alone or CIT followed by RT were included. Treatment selection was at the treating physician's discretion. Electronic medical records were reviewed for: demographics, chemotherapy regimens, radiation treatments, and PET scan data. Local IRB approval was obtained at sites. All data was distributed in a de-identified fashion. The primary outcomes were overall survival (OS), and relapse-free survival (RFS). Secondary outcomes included: response after induction CIT induction and the need for additional therapies.
Chi-square test analysis was used to compare categorical variables and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for continuous and ordinal measures. Survival curves were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared between groups via the log-rank test. Multi-variable analysis (MVA) for OS and RFS was performed using RT vs no RT, PET status post CIT (negative vs positive) and rituximab in induction (Y/N) as variables.
Results
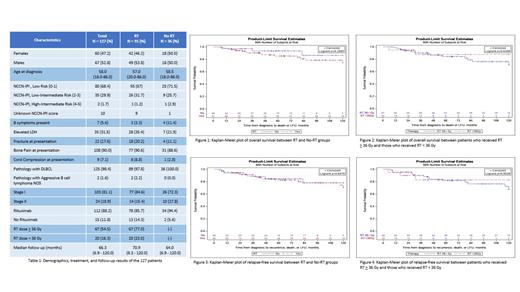
A total of 127 patients were included: 91 who received CIT and radiation (RT group), and 36 who received CIT alone (no RT group). The median age of patients at diagnosis in the RT group and no RT group was 58.5 and 57.0, respectively. For CIT, the majority of patients received R-CHOP (84%). Despite focusing on 2005-2019, a small percentage of patients (5 - 14%) in each group (RT and no RT) did not receive rituximab with their induction therapy. The OS at 10 years was 74.5% in the RT group and 86.5% in the no RT group (p = 0.29). The RFS at 10 years was 70.9% in the RT group and 78.2% in the no RT group (p = 0.85). Among the 91 patients who received RT, 67 (77.0%) received a dose of 36 Gy or higher. There was no difference in OS (p = 0.63) or RFS (p = 0.90) in patients who received > 36 Gy vs < 36 Gy of radiation. On MVA for OS, RT was not associated with improved OS, although rituximab as part of induction was (p = 0.048). On MVA for RFS, neither RT nor rituximab were associated with improved RFS. For rituximab the trend was in the direction of rituximab benefit (p = 0.11).
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that, in the rituximab era, patients with limited stage primary bone DLBCL have excellent outcomes overall. In this study, neither RFS or OS appeared to be improved with the addition of consolidative RT. Rituximab, however, was associated with improved OS on MVA. Outcomes do not appear to differ based on the dose of RT (> 36 Gy vs < 36 Gy). Our data suggests that RT may have less benefit for primary bone DLBCL in the rituximab era, although it is possible that a subset of patients may benefit from consolidative radiation therapy. A larger data set would likely be needed to evaluate this. We plan to present data regarding PET responses at the meeting.
Lunning: Acrotech: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Myeloid Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Morphosys: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy; Verastem: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy; Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Co.: Consultancy; Spectrum: Consultancy; Daiichi-Sankyo: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Legend: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy. Cashen: Secura Bio, ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy. Bartlett: Autolus: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Forty Seven: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Seagen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Caimi: XaTek: Patents & Royalties: Royalties from patents (wife); Amgen Therapeutics.: Consultancy; ADC Theraputics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Verastem: Consultancy; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Rodgers: MJH Lifesciences: Consultancy. Barr: Morphosys: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Bristol Meyers Squibb: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Abbvie/Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Epperla: Verastem: Speakers Bureau; Beigene: Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Other: Ad Board; Genzyme: Honoraria. Hill: AstraZenica: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene (BMS): Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gentenech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Epizyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; Incyte/Morphysis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Karmali: BMS/Celgene/Juno: Consultancy, Research Funding; Epizyme: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Janssen/Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Morphosys: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; EUSA: Consultancy; Takeda: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Portell: Acerta/AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Xencor: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Aptitude Health: Honoraria; Morphosys: Honoraria; Targeted Oncology: Honoraria; SeaGen: Research Funding; BeiGene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria; Kite: Honoraria, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; VelosBio: Research Funding. Fenske: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau; Servier Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; MorphoSys: Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; KaryoPharm: Consultancy; CSL Therapeutics: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Biogen: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Kite (Gilead): Speakers Bureau; Beigene: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal